Your GPU usage may be low due to outdated drivers or low-demand tasks. Low GPU usage can be caused by hardware or software issues, such as outdated drivers, insufficient workload, or faulty hardware.
It’s essential to troubleshoot these potential issues to optimize your GPU performance. Outdated drivers can hinder the GPU’s full potential, while running low-demand tasks may not fully utilize the GPU’s capabilities. Additionally, faulty hardware can also impact GPU usage. By identifying and addressing these issues, you can improve your GPU’s performance and enhance your overall system efficiency.
Regular maintenance and updates are crucial to ensuring your GPU operates at its optimal capacity, delivering the best performance for your computing needs.

Credit: www.hp.com
Common Reasons For Low Gpu Usage
When your GPU utilization is inexplicably low, it can lead to suboptimal performance and undermine the potential of your graphics card. Identifying the root causes of low GPU usage is crucial for ensuring an efficient and smooth user experience. This section delves into several common reasons that could be behind the low GPU usage.
Software Conflicts
Conflicting software can act as a roadblock to your GPU’s full potential. Certain applications or background processes may be hogging GPU resources, causing lower utilization for other tasks. Moreover, incompatible software or drivers can create conflicts and hinder the smooth operation of the GPU. The first step in resolving this issue is to identify and eliminate these conflicts to free up the GPU for its intended tasks.
Outdated Drivers
Outdated GPU drivers are a prevalent cause of low GPU usage. Incompatible or outdated drivers can result in underutilization of the GPU. It is crucial to regularly update your GPU drivers to ensure compatibility with the latest software and optimizations. Keeping the drivers up to date can help resolve this issue, improving GPU performance and overall system stability.
Power Management Settings
The power management settings in your system can also dampen GPU usage. Inappropriate power settings may prioritize energy efficiency over performance, leading to reduced GPU utilization. Adjusting the power settings to favor performance can help address this issue and unleash the full potential of your GPU.
Optimizing Your Gpu Usage
Check For Background Processes
One of the main reasons for low GPU usage could be background processes consuming system resources. Use Task Manager to identify and close any unnecessary programs running in the background.
Adjust Power Settings
Ensure your power settings are optimized for high performance by adjusting the power plan settings in the Control Panel. Using the “High Performance” power plan can help maximize GPU usage.
Update Graphics Drivers
Outdated or faulty graphics drivers can lead to low GPU usage. Regularly updating your graphics drivers can address this issue and ensure optimal performance.
Optimize In-game Settings
Adjust in-game settings such as resolution, texture quality, and anti-aliasing to maximize GPU usage without compromising visual quality. Lower unnecessary graphics settings that may strain the GPU unnecessarily.
Overclocking Your Gpu
Discover the reasons behind low GPU usage and learn how to overclock your GPU to maximize its performance. Increase your GPU utilization and experience smoother gaming and faster rendering speeds.
Understanding Gpu Overclocking
When it comes to maximizing the performance of your graphics processing unit (GPU), overclocking is a popular technique that can significantly enhance its capabilities. Overclocking involves increasing the clock speed of your GPU beyond its default settings, pushing it to operate at higher frequencies. This can lead to improved gaming and rendering performance, enabling you to achieve smoother graphics, faster frame rates, and reduced loading times. However, before you delve into the world of overclocking, it is essential to understand the risks involved and take necessary precautions to ensure the longevity of your GPU.Risks And Precautions
Overclocking your GPU can yield impressive results, but it also comes with some risks. Increasing the clock speed generates additional heat, which can lead to overheating if not properly managed. This can result in system instability, crashes, or even permanent damage to your GPU. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to take appropriate precautions. 1. Ensure Adequate Cooling: When you overclock your GPU, you must ensure sufficient cooling to dissipate the additional heat generated. This can be accomplished by using high-quality cooling solutions such as aftermarket graphics card coolers, case fans, or liquid cooling systems. Proper airflow inside your computer case can help maintain optimal temperatures and prevent overheating. 2. Gradually Increase Clock Speed: When overclocking your GPU, it is essential to proceed gradually. Incrementally increase the clock speed and test the stability of your system after each adjustment. This allows you to find the highest stable overclock while avoiding sudden crashes or system instability. 3. Monitor Temperatures: Keeping a constant eye on the temperatures of your GPU is vital during overclocking. Utilize GPU monitoring software to track the temperature readings in real-time. If your GPU starts reaching unsafe temperatures, reduce the clock speed or adjust your cooling setup accordingly.Step-by-step Overclocking Guide
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you overclock your GPU effectively: 1. Research: Before starting the overclocking process, conduct thorough research to understand your specific GPU model, its capabilities, and limitations. Familiarize yourself with the recommended voltage range and clock speeds to ensure a safe overclock. 2. Install GPU Overclocking Software: Download and install a reliable GPU overclocking software such as MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, or ASUS GPU Tweak. These tools will provide you with the necessary controls to adjust clock speeds, voltages, and fan settings. 3. Test Your Default Settings: Before making any changes, run benchmarking software to establish a baseline performance of your GPU at default settings. This will help you gauge the improvements achieved through overclocking. 4. Increase Clock Speed Incrementally: Using your chosen overclocking software, begin by increasing the clock speed in small increments, such as 50MHz at a time. After each adjustment, run stability tests, such as gaming or stress-testing applications, to ensure your system can handle the increased load. 5. Monitor Temperatures and Stability: Throughout the overclocking process, closely monitor your GPU temperatures and stability. Keep an eye out for any signs of overheating or crashes. Adjust clock speeds or cooling setups as necessary to maintain safe and stable operation. 6. Test for Extended Durations: Once you have found a stable overclock, perform long-duration stress tests to ensure its reliability over extended periods. This will validate the stability of your GPU under peak loads and help identify any potential issues. Remember, every GPU is unique, and the overclocking potential may vary. Always prioritize stability, gradually push your GPU within safe limits, and cease overclocking if you experience any instability or excessive temperatures. By understanding GPU overclocking, taking necessary precautions, and following a step-by-step guide, you can successfully enhance your GPU’s performance and unlock its full potential.Monitoring And Benchmarking
Wondering why your GPU usage is low? Monitoring and benchmarking can provide insights into performance issues. By keeping an eye on hardware utilization, you can identify bottlenecks and optimize your system for better performance.
A low GPU usage can be frustrating, especially when you’re trying to maximize your system’s performance. To diagnose and address this issue, monitoring and benchmarking your GPU can provide valuable insights. This helps you understand how your GPU is performing, identify any bottlenecks, and optimize its usage for optimal performance.
Monitoring Gpu Usage
Monitoring GPU usage allows you to keep track of how effectively your graphics card is being utilized. By monitoring GPU usage in real-time, you can identify any abnormalities and ensure that your GPU is being utilized to its full potential. There are several tools and methods you can use to monitor GPU usage:
- Task Manager: In Windows, you can use the built-in Task Manager to monitor GPU usage. Simply open Task Manager, go to the Performance tab, select GPU, and monitor the GPU utilization graph.
- Third-party Software: There are many third-party software options available that provide more advanced GPU monitoring features. Software like MSI Afterburner, GPU-Z, and HWiNFO provide detailed statistics and real-time GPU monitoring.
Benchmarking Software
Benchmarking your GPU involves running tests to assess its performance and compare it with similar hardware. This helps you understand how well your GPU is performing and identify any potential issues. Here are some popular GPU benchmarking software:
| Software | Features |
|---|---|
| 3DMark | Wide range of GPU tests, including gaming simulations and stress tests |
| Unigine Heaven | Real-time GPU temperature and utilization monitoring, benchmarking, and stress testing |
| PassMark PerformanceTest | Comprehensive benchmarking tool with GPU-specific tests and comparisons |
By benchmarking your GPU using these tools, you can gain insights into its performance capabilities and address any issues that may be causing low GPU usage.
Identifying Bottlenecks
Identifying bottlenecks is crucial to understanding why your GPU usage may be low. Bottlenecks are performance limitations that can occur when one component in your system is not keeping up with the others. Here are a few common bottlenecks that may contribute to low GPU usage:
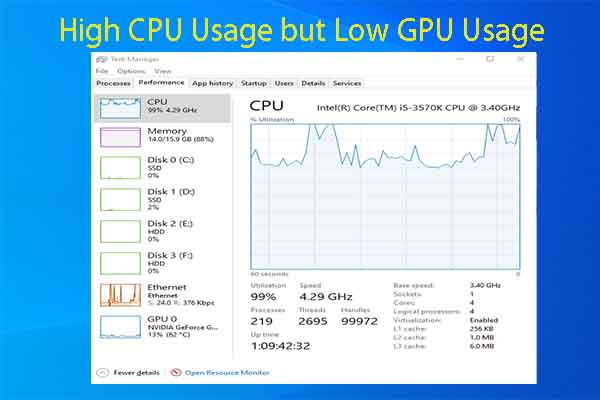
- CPU bottleneck: If your CPU is outdated or underpowered, it may not be able to keep up with your GPU’s demands, resulting in low GPU usage.
- RAM bottleneck: Insufficient RAM can limit the amount of data your GPU can process, leading to underutilization.
- Storage bottleneck: Slow or fragmented hard drives can cause delays in data transfer, impacting GPU performance.
By identifying and addressing these bottlenecks, you can optimize your system’s performance and ensure your GPU is running at its maximum potential.
Upgrading Your Gpu
The graphics processing unit (GPU) is a crucial component of any computer system responsible for rendering images, videos, and animations. If you’ve noticed that your GPU usage is consistently low, it could be an indication that it’s time for an upgrade. Upgrading your GPU can enhance your computer’s performance, allowing you to enjoy graphically-intensive tasks and games smoothly.
Assessing Your Gpu’s Limitations
Before you dive into the process of upgrading your GPU, it’s important to assess the limitations of your current GPU. Identifying these limitations will help you determine what level of upgrade is necessary for your specific needs. You can assess your GPU’s limitations through the following steps:
- Check the specifications: Find out the model and specifications of your current GPU. Look for details such as memory size, clock speeds, and CUDA or OpenCL support. This information will give you a better understanding of the capabilities and limitations of your GPU.
- Monitor performance: Use monitoring software to track your GPU’s performance while running graphically-intensive tasks or games. Pay attention to the GPU usage percentage and compare it to the performance benchmarks of similar GPUs. If your GPU usage consistently remains low even when under load, it could indicate that it’s not able to handle the demands of modern applications.
- Evaluate your needs: Consider the specific tasks you want to perform and the level of performance you desire. If you find that your current GPU falls short in meeting your needs, it might be time for an upgrade.
Choosing The Right Gpu
When it comes to selecting a new GPU, narrowing down your options can be overwhelming. However, by considering a few key factors, you can choose the right GPU that suits your requirements:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the GPU you choose is compatible with your computer’s motherboard and power supply. Check the dimensions and power requirements to avoid any compatibility issues.
- Performance vs. Price: Determine your budget and prioritize your needs. Research the performance benchmarks and reviews for different GPUs within your price range to find the best balance between performance and cost.
- Future-proofing: Consider the lifespan of the GPU and its ability to handle upcoming technologies and advancements. Opting for a GPU that can keep up with new software releases and graphical advancements can save you from needing to upgrade again in the near future.
Installation Tips And Considerations
Once you have chosen the right GPU, it’s time to install it in your system. Keep the following tips and considerations in mind to ensure a smooth installation process:
- Prepare your system: Before installation, make sure you have the appropriate tools and remove any static electricity by grounding yourself. Refer to your computer’s manual for specific instructions on how to access and remove the current GPU.
- Driver installation: Download the latest drivers for your new GPU from the manufacturer’s website. Uninstall the old drivers and install the new ones before physically installing the new GPU.
- Physical installation: Carefully insert the new GPU into the appropriate PCIe slot on your motherboard, ensuring it is properly aligned. Secure it with the necessary screws or clips, and connect the power cables if required.
- Testing and troubleshooting: After installation, boot up your system and check for any error messages or issues. Monitor the GPU’s temperature and performance for any abnormalities. If necessary, update your BIOS settings to ensure optimum compatibility.
By following these guidelines, you can upgrade your GPU effectively and enjoy improved graphics performance on your computer. Remember to research and choose a GPU that fits your specific requirements, considering factors such as compatibility, performance, and future-proofing. With a new GPU in place, you can expect smoother and more visually immersive experiences from your computer.
Credit: www.partitionwizard.com

Credit: rog.asus.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Why Is My Gpu Usage So Low
Why Is My Gpu Usage So Low?
Your GPU usage may be low due to a variety of reasons. It could be caused by outdated drivers or settings, CPU bottlenecking, or even power-saving modes. Check your GPU settings, update drivers, and ensure there are no CPU bottlenecks to address the low GPU usage issue.
What Are The Effects Of Low Gpu Usage?
Low GPU usage can result in lower gaming or rendering performance, laggy visuals, and reduced frame rates. It can also indicate inefficient utilization of your GPU’s capabilities and potential performance bottlenecks. Identifying and addressing the cause of low GPU usage can help improve overall system performance.
How Can I Increase My Gpu Usage?
To increase GPU usage, try the following:
1. Ensure your GPU drivers are up to date. 2. Optimize in-game settings for better GPU utilization. 3. Close unnecessary background applications. 4. Check for CPU bottlenecks and address them if present. 5. Consider overclocking your GPU (if supported) for higher performance. Remember, the actual increase in GPU usage may vary depending on your specific hardware and software configuration.
Conclusion
Low GPU usage can be caused by various factors, such as outdated drivers, power settings, or software conflicts, ultimately affecting your computer’s performance. By troubleshooting and addressing these issues, you can optimize your GPU usage and enhance your gaming or graphic-intensive experience.
Stay up to date with the latest GPU drivers and ensure your power settings align with your usage requirements. Remember, a well-maintained GPU leads to better overall system performance.



