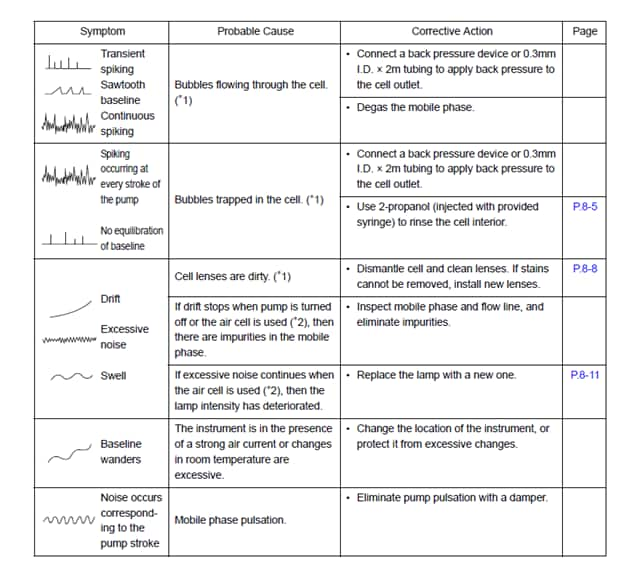
HPLC troubleshooting involves identifying and resolving issues that affect chromatographic performance. Common problems include baseline noise, peak tailing, and pressure fluctuations.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful analytical tool used in various industries. It helps in separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in a mixture. Despite its effectiveness, users often encounter issues that can affect the quality of results. Baseline noise, peak tailing, and pressure fluctuations are frequent challenges.
Understanding these problems and their solutions can save time and improve efficiency. Proper maintenance, systematic troubleshooting, and using high-quality reagents can enhance HPLC performance. This guide provides practical tips to address common HPLC problems, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
Common Issues In Hplc
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a vital tool in laboratories. It can face various issues that affect results. Here are some common problems you might encounter.
Baseline Noise
Baseline noise can disturb the clarity of your results. Several factors can cause this:
- Mobile Phase Impurities: Ensure the mobile phase is free from impurities.
- Detector Issues: Check for any problems with the detector.
- Column Problems: Verify the column is clean and in good condition.
Regular maintenance helps reduce baseline noise.
Peak Tailing
Peak tailing can make data interpretation difficult. Common causes include:
| Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
| Column Overloading | Reduce sample amount injected into the column. |
| Interaction with Stationary Phase | Use a different column with a suitable stationary phase. |
| Poor Mobile Phase Preparation | Ensure mobile phase is prepared accurately. |
Addressing these issues can improve peak shapes.
Retention Time Shifts
Retention time shifts can lead to inaccurate results. They may be caused by:
- Temperature Fluctuations: Keep the column oven at a consistent temperature.
- Flow Rate Variations: Ensure the pump delivers a stable flow rate.
- Column Aging: Replace old or damaged columns regularly.
Maintaining a stable environment can minimize retention time shifts.
Credit: www.ssi.shimadzu.com
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is crucial for the optimal performance of your HPLC system. Regular upkeep minimizes downtime and ensures accurate results. Let’s explore some key aspects of preventive maintenance.
Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning is essential for maintaining the efficiency of your HPLC system. Contaminants can build up over time and affect performance.
- Flush the system with a suitable solvent.
- Clean the injection port regularly.
- Replace the mobile phase frequently.
Cleaning the injection port prevents blockages. Use a lint-free cloth to wipe surfaces.
Component Inspections
Regular component inspections help identify wear and tear early. Inspecting components can prevent unexpected failures.
- Check the pump seals and pistons.
- Inspect the column for any damages.
- Examine the detector for signal consistency.
Replace worn-out parts immediately. This action ensures the system runs smoothly.
Below is a table summarizing the frequency of inspections:
| Component | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|
| Pump Seals | Every 3 months |
| Column | Every 6 months |
| Detector | Monthly |
Following these guidelines will help your HPLC system last longer. Stay proactive and keep your system in top shape.
Column Performance
Understanding column performance in HPLC is crucial for accurate results. A well-maintained column ensures efficiency and reliability. This section covers essential tips on choosing and storing columns.
Choosing The Right Column
Selecting the right column is vital for optimal HPLC performance. Consider the following factors when choosing a column:
- Particle size: Smaller particles offer better resolution but higher backpressure.
- Column length: Longer columns provide better separation but take more time.
- Inner diameter: Narrower diameters improve sensitivity but require precise handling.
- Stationary phase: Choose based on the chemical properties of your analytes.
Each factor affects the overall performance and results of your analysis.
Column Storage Tips
Proper storage extends the life of your HPLC columns. Follow these tips for effective storage:
- Flush the column: Clean the column with an appropriate solvent after use.
- Seal properly: Cap both ends of the column to prevent contamination.
- Store upright: Keep the column in a vertical position to avoid air bubbles.
- Temperature control: Store columns at a stable, cool temperature.
Proper storage ensures the column remains in good condition for future use.
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Resolution and backpressure |
| Column Length | Separation and time |
| Inner Diameter | Sensitivity and handling |
| Stationary Phase | Chemical compatibility |
HPLC Mobile Phase Management
Proper mobile phase management is crucial in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). It impacts the accuracy and reproducibility of your results. This section will cover essential aspects of mobile phase management.
Solvent Preparation
Quality solvents are key for reliable HPLC analysis. Always use high-purity solvents to avoid contamination. Measure solvents accurately for consistency. Follow these steps for solvent preparation:
- Use clean, dry glassware.
- Measure each solvent with precision.
- Mix solvents thoroughly.
Keep prepared solvents in airtight containers. Label them with the date and solvent type. This helps maintain solvent integrity.
Degassing Techniques
Degassing removes dissolved gases from the mobile phase. Gases can cause bubbles and noise in your HPLC system. There are several degassing methods:
- Vacuum Degassing: Apply a vacuum to the solvent container.
- Ultrasonic Degassing: Use an ultrasonic bath to remove gases.
- Helium Sparging: Bubble helium through the solvent.
Each method has its benefits. Choose one that fits your lab setup. Proper degassing ensures stable baselines and accurate results.
HPLC System Suitability Tests
System Suitability Tests ensure your HPLC system works properly. These tests confirm that your system can produce reliable and accurate results. Regular checks are essential for maintaining the system’s performance.
Performance Criteria
Performance criteria are specific metrics. They help assess the system’s efficiency. Common criteria include:
- Retention Time: Measures how long a compound stays in the column.
- Resolution: Determines the separation between two peaks.
- Theoretical Plates: Indicates column efficiency.
- Tailing Factor: Shows peak symmetry.
Each metric has set limits. Results must fall within these limits. If not, troubleshoot the system immediately.
Documentation Practices
Proper documentation is crucial. It ensures traceability and compliance. Follow these practices:
- Record all test results.
- Note any deviations or errors.
- Log corrective actions taken.
- Use standardized forms or templates.
Keep records organized and accessible. This helps in future audits and reviews. Consistent documentation maintains system integrity.
| Criteria | Acceptable Range |
|---|---|
| Retention Time | ± 2% of standard |
| Resolution | > 1.5 |
| Theoretical Plates | > 2000 |
| Tailing Factor | < 2.0 |
Ensure all criteria meet the acceptable range. This confirms system suitability.
Detector Issues
Issues with detectors can significantly impact your HPLC results. It’s crucial to identify and resolve these problems swiftly. This guide will help you troubleshoot common detector issues effectively.
Uv-vis Detector Troubles
The UV-Vis detector is widely used in HPLC. Yet, it can face several issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Baseline Drift: Caused by temperature changes. Ensure consistent lab temperature.
- Noise: May result from a dirty flow cell. Clean the flow cell regularly.
- Low Sensitivity: Check the lamp’s intensity. Replace the lamp if needed.
Fluorescence Detector Tips
The fluorescence detector offers high sensitivity. But it can encounter specific issues:
- Quenching: Occurs due to high analyte concentration. Dilute the sample.
- Photobleaching: Causes signal loss over time. Use lower excitation energy.
- Interference: From impurities. Use high-purity solvents and clean samples.
HPLC Software Troubleshooting
Navigating the complexities of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) can be challenging. Software issues often add to these challenges. Understanding how to troubleshoot software problems is key to ensuring smooth HPLC operations. This guide covers common software issues and how to resolve them.
Integration Errors
Integration errors can disrupt your HPLC analysis. These errors occur when the software fails to correctly interpret the chromatogram. To resolve this, follow these steps:
- Verify peak parameters: Check the integration settings. Ensure they match your sample’s characteristics.
- Review baseline settings: Incorrect baseline settings can cause integration issues. Adjust as needed.
- Software updates: Ensure your HPLC software is up-to-date. Updates often fix bugs.
If these steps don’t solve the problem, consider consulting the software manual. Documentation often provides specific solutions for your software version.
Data Export Problems
Data export problems can hinder your ability to share or analyze results. These issues often stem from incorrect settings or software bugs. To fix data export problems:
- Check export settings: Ensure the export format matches your needs. Common formats include CSV, PDF, and Excel.
- File permissions: Verify you have the necessary permissions to export files.
- Software compatibility: Ensure your export file is compatible with the target software.
If you still face issues, reinstalling the software might help. This can resolve underlying bugs causing the export problems.

Credit: ymc.eu
Sample Preparation Tips
Preparing your sample correctly is vital for accurate HPLC results. Improper preparation can lead to various issues. These issues can affect both the separation and detection phases. Below are two critical aspects of sample preparation: filtration and dilution.
Filtration Methods
Filtering your samples removes particulates that can clog the HPLC system. This ensures a smooth flow and reliable results.
- Syringe Filters: These are ideal for small volumes. Use a 0.45 µm or 0.2 µm pore size.
- Membrane Filters: Suitable for larger volumes. Choose the material based on your sample’s compatibility.
- Vacuum Filtration: Efficient for high-volume samples. It uses a vacuum pump to speed up the process.
Dilution Techniques
Diluting your samples helps in achieving better peak shapes and reducing matrix effects. Correct dilution can also prevent overloading of the column.
- Serial Dilution: Gradually dilute your sample step-by-step. This method ensures accuracy and consistency.
- Direct Dilution: Mix the sample with the solvent in a single step. It’s quick but less precise.
- Matrix Matching: Dilute your sample in a similar matrix as your mobile phase. This helps in achieving better chromatographic performance.
Use these sample preparation tips to enhance your HPLC analysis. Proper filtration and dilution ensure accurate and reliable results.
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Troubleshooting Problems In Hplc?
Common HPLC troubleshooting problems include pressure fluctuations, baseline noise, peak tailing, and ghost peaks. Regular maintenance and calibration help prevent these issues.
What Are The Common Peak Problems In Hplc And Their Causes?
Common HPLC peak problems include peak tailing, fronting, broadening, and splitting. Causes include column contamination, improper mobile phase, and sample overload.
What Could Lead To Inaccurate Result In Hplc?
Contaminated samples or solvents, improper calibration, column degradation, and incorrect mobile phase composition can cause inaccurate HPLC results.
How Do You Resolve Negative Peaks In Hplc?
Resolve negative peaks in HPLC by checking for system leaks, ensuring proper mobile phase composition, and eliminating air bubbles. Use fresh solvents and maintain a clean column to prevent contamination. Regularly calibrate and maintain equipment to ensure accurate readings.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting HPLC issues can save time and enhance results. Follow the tips outlined in this guide. Ensure regular maintenance and calibration. Always check solvent quality and column condition. Stay proactive to avoid common pitfalls. Happy experimenting with your HPLC system!