Diaphragm pump troubleshooting involves identifying issues like leaks, loss of pressure, or irregular flow. Common problems include damaged diaphragms, clogged valves, or air supply issues.
Diaphragm pumps are essential in many industries for their efficiency and reliability. These pumps handle various fluids, including aggressive chemicals, viscous substances, and slurries. Despite their robustness, diaphragm pumps can experience issues that disrupt operations. Common problems include leaks, loss of pressure, and irregular flow.
Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Damaged diaphragms, clogged valves, or air supply issues often contribute to these problems. Regular maintenance and timely repairs ensure diaphragm pumps operate smoothly, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity. Understanding these common issues helps in maintaining optimal performance.
Common Diaphragm Pump Issues
Diaphragm pumps are vital for many industries. Sometimes, they face common issues. Identifying these problems early can save time and money. This guide will help you understand and troubleshoot common diaphragm pump issues.
No Flow
One common issue is no flow. The pump runs, but nothing comes out. This can happen due to several reasons.
- Check if the inlet and outlet valves are open.
- Ensure there is no airlock in the pump.
- Inspect the suction line for any blockages.
- Verify the diaphragm is not damaged or worn out.
Addressing these points can often restore the flow.
Low Pressure
Another issue is low pressure. The pump works but the pressure is low. This can lead to inefficient operations.
- Check for leaks in the system.
- Ensure the pressure relief valve is set correctly.
- Inspect the diaphragm for any signs of wear.
- Verify the check valves are functioning properly.
Fixing these issues can often improve the pressure.

Credit: cannonwater.com
Identifying Blockages of Diaphragm Pump
Diaphragm pumps are essential in various industries. They ensure smooth fluid transfer. Sometimes, blockages occur. Identifying and resolving these blockages is crucial. This section will focus on Identifying Blockages in diaphragm pumps.
Inlet Blockages
Inlet blockages are common. They restrict fluid entry. This impacts the pump’s efficiency. Follow these steps to identify inlet blockages:
- Check the inlet screen for debris.
- Ensure the inlet hose is clear.
- Inspect the inlet valve for clogs.
Use a flashlight. Look inside the inlet. Remove any visible debris. Inlet blockages can cause significant problems. Regular checks can prevent issues.
Outlet Blockages
Outlet blockages hinder fluid exit. This can cause back pressure. Follow these steps to identify outlet blockages:
- Examine the outlet hose for obstructions.
- Inspect the outlet valve for blockages.
- Check for kinks or bends in the hose.
Use a small brush. Clean the outlet valve. Ensure smooth fluid flow. Outlet blockages can damage the pump. Routine maintenance is key.
| Blockage Type | Common Signs | Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet Blockage | Reduced flow, unusual noises | Check screen, inspect hose and valve |
| Outlet Blockage | Back pressure, fluid leakage | Examine hose, clean valve |
Regular inspection prevents blockages. Maintain your diaphragm pump. Ensure optimal performance.
Diaphragm Pump Air Supply Problems
Diaphragm pumps need a proper air supply to work well. Air supply problems can stop your pump from working. Let’s look at some common air supply problems.
Inadequate Air Pressure
Inadequate air pressure can cause your pump to work poorly. This happens if the air pressure is too low. Check your air compressor settings. Make sure the pressure matches the pump’s needs.
Here is a simple table to guide you:
| Pressure (PSI) | Effect on Pump |
|---|---|
| Below 20 PSI | Pump may not start |
| 20-40 PSI | Pump runs but slowly |
| 40-60 PSI | Optimal performance |
Always check the pressure gauge. Adjust it if needed. Proper air pressure ensures smooth operation.
Air Leaks
Air leaks are another common problem. Leaks reduce the air supply. This makes the pump less efficient. Look for leaks in the air hoses. You can use soapy water to find leaks. Bubbles will form where there is a leak.
Fixing leaks is easy. Follow these steps:
- Turn off the air supply.
- Check all air hoses and fittings.
- Tighten any loose connections.
- Replace damaged hoses.
Regular checks can prevent air leaks. This keeps your pump running smoothly.

Credit: www.pumpsandsystems.com
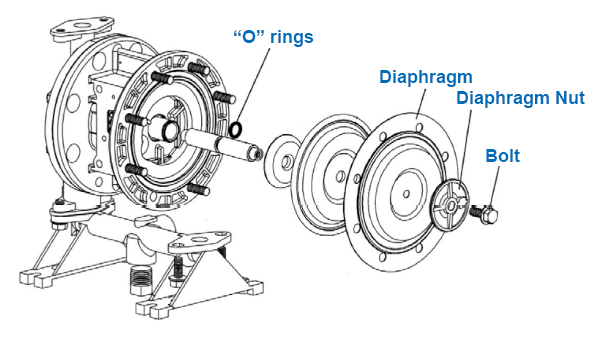
Diaphragm Damage
Diaphragm pumps are essential for many industries. They move fluids efficiently. But, diaphragm damage can stop the entire system. This section will help you identify damage and fix it.
Signs Of Wear
Identifying wear early can save you time and money. Look for these signs:
- Cracks or Tears: Visible cracks mean the diaphragm is damaged.
- Reduced Flow: Less fluid flow points to diaphragm wear.
- Leaks: Fluid leaks indicate a compromised diaphragm.
- Noise: Unusual sounds suggest diaphragm problems.
Replacement Steps
Replacing a damaged diaphragm is straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Shut Down: Turn off the pump and disconnect power.
- Drain: Remove any fluid inside the pump.
- Disassemble: Open the pump housing carefully.
- Remove: Take out the old diaphragm.
- Inspect: Check other parts for wear.
- Install: Place the new diaphragm in position.
- Reassemble: Put the pump back together.
- Test: Run the pump to ensure it works properly.
Keeping your diaphragm pump in top shape ensures smooth operations. Regular checks and timely replacements are key.
Check Valve Malfunctions
Diaphragm pumps are essential in many industries. A common issue is check valve malfunctions. These valves regulate fluid flow. They ensure the pump operates efficiently. If a check valve fails, it can halt operations. Below are steps for troubleshooting check valve malfunctions.
Valve Inspection
Start by inspecting the check valve. Look for visible damage. Check for cracks or wear. Inspect the valve seat for debris. A damaged valve can cause leaks.
Use a flashlight for better visibility. Ensure the valve is seated properly. Misalignment can lead to failure. If the valve seems stuck, try moving it gently.
Cleaning Procedures
Dirt and debris can block check valves. Cleaning is crucial. Follow these steps for a thorough cleaning:
- Remove the valve from the pump.
- Rinse with clean water.
- Use a soft brush to scrub away debris.
- Check for any remaining dirt.
- Dry the valve completely.
For stubborn dirt, use a mild detergent. Avoid harsh chemicals. They can damage the valve material. Rinse thoroughly to remove soap residue.
| Step | Action | Tools Needed |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Remove the valve | Wrench |
| 2 | Rinse with water | Water source |
| 3 | Scrub debris | Soft brush |
| 4 | Check for dirt | Flashlight |
| 5 | Dry the valve | Clean cloth |
Regular inspection and cleaning can prevent check valve malfunctions. This ensures your diaphragm pump runs smoothly.
Diaphragm Pump Fluid Compatibility Issues
Diaphragm pumps are versatile and handle various fluids. But, fluid compatibility issues can arise. These issues can damage the pump and disrupt operations.
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions between pump materials and fluids can be harmful. These reactions can cause corrosion, swelling, or even leaks. Always check the chemical resistance of your pump materials.
For example, acids can corrode metal parts. Organic solvents may swell rubber diaphragms. Always refer to a chemical compatibility chart for guidance.
| Chemical | Compatible Materials | Incompatible Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid | PTFE, PVDF | Steel, Aluminum |
| Benzene | Viton, PTFE | EPDM, Natural Rubber |
Material Selection
Choosing the right material for your pump parts is essential. Different materials offer varying levels of compatibility with fluids.
Common diaphragm materials include PTFE, EPDM, and Viton. PTFE resists most chemicals but is less flexible. EPDM is good for water-based fluids but not for oils. Viton handles oils and solvents well.
- PTFE: Resistant to most chemicals, less flexible.
- EPDM: Good for water-based fluids, not for oils.
- Viton: Handles oils and solvents well.
Consider the fluid type and operating conditions. This ensures long pump life and efficient operation.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance ensures diaphragm pumps perform efficiently and last longer. Follow these tips to keep your pump in top condition.
Regular Inspections
Regular inspections help identify issues early. Check for leaks and unusual noises. Inspect all connections and fittings. Make sure there are no loose parts.
- Inspect the diaphragm for wear and tear.
- Check the pump housing for cracks.
- Ensure all bolts and nuts are tight.
Lubrication Points
Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear. Lubricate according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Use the recommended lubricant type.
| Component | Lubrication Frequency | Lubricant Type |
|---|---|---|
| Bearings | Monthly | Grease |
| Piston Rods | Bi-monthly | Oil |
| Seals | Quarterly | Silicone Grease |
Over-lubrication can cause damage. Follow the specified amounts. Always clean old lubricant before applying new.
Credit: www.carlisleft.co.jp
When To Call A Professional
Diaphragm pumps are reliable but can sometimes face issues. Some problems are easy to fix at home. But, other problems need a professional’s help. Knowing when to call a professional can save time and money. Below are key situations when expert help is needed.
Complex Repairs
Some repairs are too complex for a beginner. These include electrical issues and motor failures. Professionals have the right tools and skills. They can fix these problems safely and quickly.
- Electrical issues
- Motor failures
- Severe leaks
Trying to fix these yourself can cause more damage. It may also void your warranty. Always call a professional for complex repairs.
Warranty Considerations
Most diaphragm pumps come with a warranty. This warranty protects you from defects. But, doing your own repairs can void this warranty. Check your warranty terms before attempting any fixes.
| Repair Type | Warranty Status |
|---|---|
| Minor issues | Usually covered |
| Major repairs | Requires professional |
Always call a professional for repairs covered by the warranty. This ensures your pump remains protected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Common Problem With Diaphragm Pumps?
Diaphragm pumps often face issues like diaphragm wear, air valve clogging, and leakage. Regular maintenance minimizes these problems.
Why Is My Diaphragm Water Pump Not Working?
Your diaphragm water pump might not work due to clogged filters, air leaks, power supply issues, or a faulty pressure switch. Ensure proper maintenance and check connections.
Why Is My Diaphragm Pump Pulsating?
Your diaphragm pump is pulsating due to air in the system, a clogged suction line, or a damaged diaphragm. Check for air leaks, clean the suction line, and inspect the diaphragm for wear. Regular maintenance can prevent pulsation issues.
What Happens If You Run A Diaphragm Pump Dry?
Running a diaphragm pump dry can cause damage. The pump may overheat, leading to seal failure and component wear.
Conclusion
Understanding diaphragm pump troubleshooting ensures optimal performance. Regular maintenance can prevent many common issues. Follow the steps outlined for effective troubleshooting. Proper care extends the lifespan of your pump. Stay proactive and address problems promptly. This will save time and costs, ensuring smooth operations.
Happy pumping!



